# 分布式限流设计与实现
# 常见限流算法
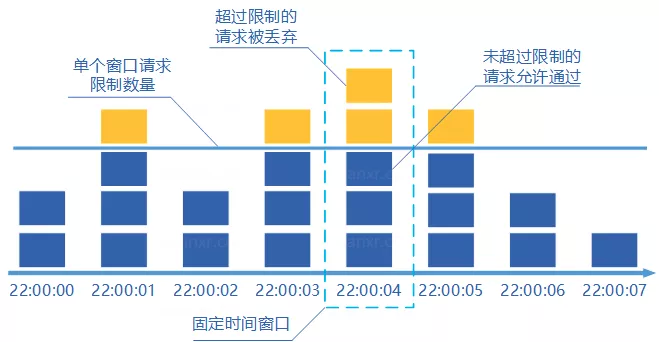
# 固定窗口计数
固定窗口计数器算法概念如下:
- 将时间划分为多个窗口;
- 在每个窗口内每有一次请求就将计数器加一;
- 如果计数器超过了限制数量,则本窗口内所有的请求都被丢弃当时间到达下一个窗口时,计数器重置。
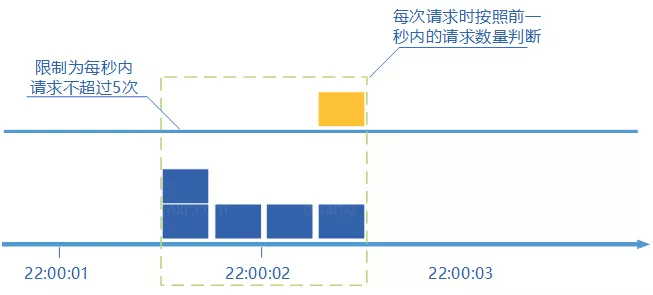
# 滑动窗口计数
滑动窗口计数器算法概念如下:
- 将时间划分为多个区间;
- 在每个区间内每有一次请求就将计数器加一维持一个时间窗口,占据多个区间;
- 每经过一个区间的时间,则抛弃最老的一个区间,并纳入最新的一个区间;
- 如果当前窗口内区间的请求计数总和超过了限制数量,则本窗口内所有的请求都被丢弃。
# 漏桶算法
漏桶算法概念如下:
- 将每个请求视作 "水滴" 放入 "漏桶" 进行存储;
- “漏桶 "以固定速率向外" 漏 "出请求来执行如果" 漏桶 "空了则停止" 漏水”;
- 如果 "漏桶" 满了则多余的 "水滴" 会被直接丢弃。
漏桶算法多使用队列实现,服务的请求会存到队列中,服务的提供方则按照固定的速率从队列中取出请求并执行,过多的请求则放在队列中排队或直接拒绝。
漏桶算法的缺陷也很明显,当短时间内有大量的突发请求时,即便此时服务器没有任何负载,每个请求也都得在队列中等待一段时间才能被响应。

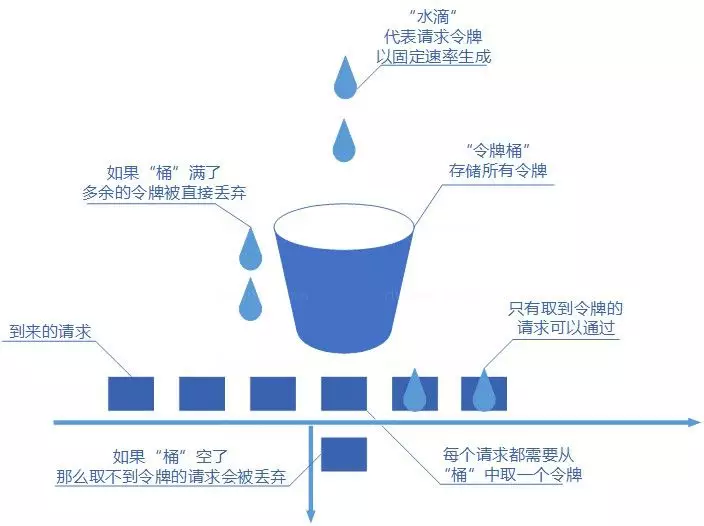
# 令牌桶
令牌桶算法概念如下:
- 令牌以固定速率生成;
- 生成的令牌放入令牌桶中存放,如果令牌桶满了则多余的令牌会直接丢弃,当请求到达时,会尝试从令牌桶中取令牌,取到了令牌的请求可以执行;
- 如果桶空了,那么尝试取令牌的请求会被直接丢弃。
# 通过 Nginx + Lua + Redis 实现分布式限流
踩坑记录,如果只是学习的话,不建议尝试使用自己编译 Nginx + LuaJit + lua-nginx-module
踩坑记录已经有其他人记录下来了,https://www.cnblogs.com/yulibostu/articles/10529989.html他的三个坑我都踩过了
# 环境配置
# 安装 Redis 安装 Lua
略
# 安装 openresty
openresty 是一个基于 NGINX 的可伸缩的 Web 平台
官网: https://openresty.org/cn/installation.html
安装教程:https://openresty.org/cn/linux-packages.html#ubuntu
使用方式
# 启动 | |
openresty | |
# 重新加载 | |
openresty -s reload | |
# 关闭 | |
openresty -s stop |
# 业务流程
GITHUB:https://github.com/Twelveeee/ratelimiter-go/tree/master/lua-ngx-ratelimiter
根据 接口 URI + 请求参数caller 进行限流

# 配置
所有 _config.lua 结尾的代码文件都是是用于配置的
新增限流接口配置: limited_api_config.lua
设置 caller 参数白名单配置]caller_whitelist_config.lua
设置限流 key 黑名单配置:blocked_keys_config.lua
对特定 caller 的请求接口进行单独设置限流阈值配置 token_bucket_config.lua
# 测试
启动服务:在当前目录执行
./dev/start.sh
停止服务:
./dev/stop.sh
修改后重新加载服务:
./dev/reload.sh
# 普通正常 post 请求,不在 limited_api_config 中,不会触发限频逻辑 | |
# 正常返回 hello world | |
curl http://localhost:8881/_dev_api -d '{"seqId": "xx-xx-xx", "caller":"_dev_ashin"}' | |
# 普通正常 get 请求,不在 limited_api_config 中,不会触发限频逻辑 | |
# 正常返回 hello world | |
curl "http://localhost:8881/_dev_api?seqId=xx-xx-xx&caller=_dev_ashin" | |
# 请求生成的 key 触发黑名单 (key 对应 blocked_keys_config 中的 `ratelimiter:/_dev_api/blocked:1`) | |
# 返回对应的错误 json | |
curl http://localhost:8881/_dev_api/blocked -d '{"seqId": "xx-xx-xx", "caller":"1"}' | |
# 请求的 uri 匹配 limited_api_config 中的 `/_dev_api/limited` 触发限频逻辑 | |
# caller 和 uri 不匹配 token_bucket_config 中的配置,应该采用 default 配置 | |
curl http://localhost:8881/_dev_api/limited -d '{"seqId": "xx-xx-xx", "caller":"mayday"}' | |
# 触发特殊限流配置 每秒只能访问一次 快速手动执行可以触发限频 返回对应的错误 json | |
curl http://localhost:8881/_dev_api/limited -d '{"seqId": "xx-xx-xx", "caller":"_dev_ashin"}' | |
# 请求参数 caller 触发白名单 ( caller 对应 caller_whitelist_config 中的 _dev_whitelist ),即使是请求限流接口也不会触发限频逻辑 | |
# 正常返回 hello world | |
curl http://localhost:8881/_dev_api/limited -d '{"seqId": "xx-xx-xx", "caller":"_dev_whitelist"}' |
# 重要代码逻辑
-- 业务相关的限流 key 相关方法 | |
local json = require "cjson" | |
local utils = require "utils" | |
local blocked_keys = require "blocked_keys_config" | |
local limited_apis = require "limited_api_config" | |
local whitelist = require "caller_whitelist_config" | |
local _M = { | |
separator = ":", | |
prefix = "ratelimiter", | |
} | |
-- 生成限流 key | |
-- ratelimiter:region:api:caller:ip | |
function _M:new() | |
ngx.log(ngx.DEBUG, "ratelimiter: new key module") | |
local o = {} | |
setmetatable(o, {__index = self}) | |
local host = utils.str_split(ngx.var.host, ".")[1] | |
local client_ip = utils.get_client_ip() or "" | |
-- 获取请求参数 | |
local caller = "" | |
local args = utils.get_req_args() | |
if args ~= nil then | |
caller = args["caller"] or "" | |
end | |
local api_name = ngx.var.uri | |
if ngx.var.request_uri ~= nil and ngx.var.request_uri ~= "" then | |
local r = utils.str_split(ngx.var.request_uri, "?") | |
if #r >= 1 then | |
api_name = r[1] | |
end | |
end | |
o.api_name = api_name | |
o.caller = caller | |
o.client_ip = client_ip | |
o.key = o.prefix .. o.separator .. api_name .. o.separator .. caller | |
-- ratelimiter:localhost:/_dev_api/limited::127.0.0.1 | |
ngx.log(ngx.INFO, "ratelimiter: gen a new limit key -> " .. o.key) | |
return o | |
end | |
-- 判断黑名单 | |
function _M:is_in_blacklist() | |
ngx.log(ngx.INFO, "ratelimiter: check blacklist for key:" .. self.key) | |
-- key 在 blocked_keys 中表示被拉黑 | |
if blocked_keys[self.key] ~= nil then | |
ngx.log(ngx.ERR, "ratelimiter: key=" .. self.key .. " hit blocked key") | |
return true | |
end | |
return false | |
end | |
-- 判断是否是需要限流的接口 | |
function _M:is_limited_api() | |
ngx.log(ngx.INFO, "ratelimiter: check is limited api for key=" .. self.key) | |
-- api_name 在 limited_apis 中表示需要进行限流检查 | |
if limited_apis[self.api_name] ~= nil then | |
ngx.log(ngx.WARN, "ratelimiter: key=" .. self.key .. " hit limited api") | |
return true | |
end | |
ngx.log(ngx.INFO, "ratelimiter: api=" .. self.api_name .. " does not need to be limited.") | |
return false | |
end | |
-- 判断白名单 | |
function _M:is_in_whitelist() | |
ngx.log(ngx.INFO, "ratelimiter: check whitelist for key=" .. self.key) | |
local caller = '' | |
local args = utils.get_req_args() | |
if args ~= nil then | |
caller = args['caller'] or '' | |
end | |
-- 请求参数中 caller 值在白名单中的全部放行 | |
if whitelist[caller] ~= nil then | |
ngx.log(ngx.WARN, "ratelimiter: caller=" .. caller .. " hit whitelist") | |
return true | |
end | |
return false | |
end | |
return _M |
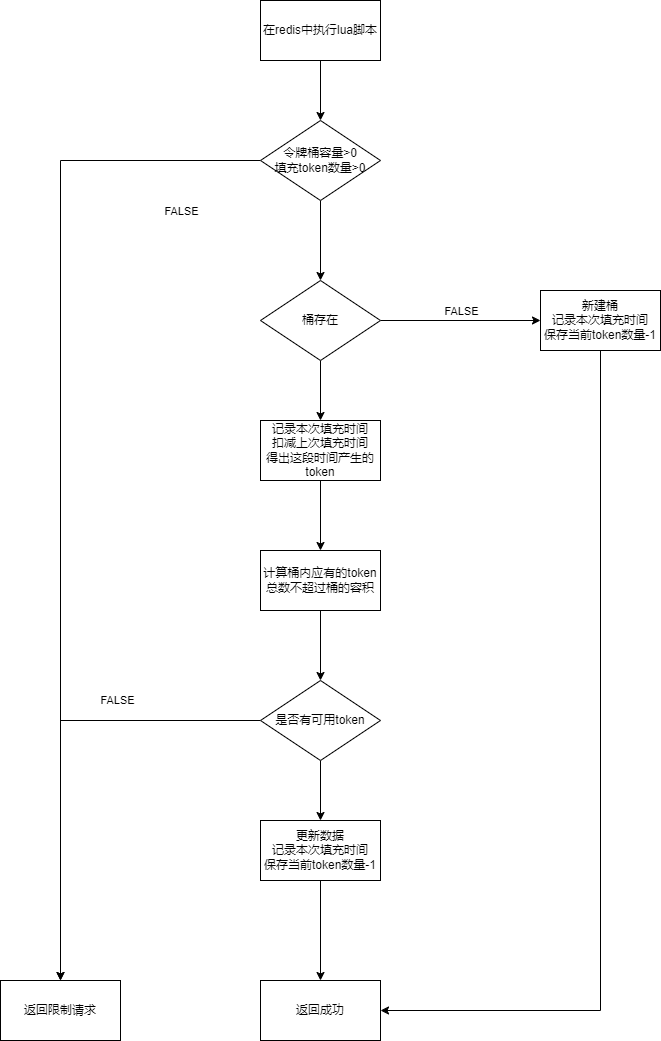
在 redis 里面使用 eval 也是原子性的,并发安全。
流程如下
-- 令牌桶限流相关逻辑实现,返回 1 表示被限流, 0 表示不限流 | |
-- 使用 redis eval 执行令牌桶相关运算逻辑的脚本内容获取返回值,借助 eval 的原子性保证并发安全 | |
-- 脚本的原子性: Redis 使用单个 Lua 解释器去运行所有脚本,并且, Redis 也保证脚本会以原子性 (atomic) 的方式执行:当某个脚本正在运行的时候,不会有其他脚本或 Redis 命令被执行。这和使用 MULTI / EXEC 包围的事务很类似。 | |
local redis = require "resty.redis" | |
local redis_config = require "redis_config" | |
local bucket_config = require "token_bucket_config" | |
local utils = require "utils" | |
local _M = {} | |
-- 创建令牌桶,每一个 key 拥有一个桶 | |
function _M:new(limit_key) | |
ngx.log(ngx.INFO, "ratelimiter: new token bucket module for key=" .. limit_key.key) | |
local o = {} | |
setmetatable(o, {__index = self}) | |
o.key = limit_key.key | |
local default_config = bucket_config['default'] | |
o.fill_count = default_config.fill_count | |
o.interval_microsecond = default_config.interval_microsecond | |
o.bucket_capacity = default_config.bucket_capacity | |
o.expire_second = default_config.expire_second | |
local special_config_name = limit_key.caller .. ":" .. limit_key.api_name | |
local special_config = bucket_config[special_config_name] | |
if special_config ~= nil then | |
o.fill_count = special_config.fill_count | |
o.interval_microsecond = special_config.interval_microsecond | |
o.bucket_capacity = special_config.bucket_capacity | |
o.expire_second = special_config.expire_second | |
end | |
return o | |
end | |
-- 判断 key 是否被限流 | |
-- 使用 redis eval 执行脚本代码来保证原子性 | |
function _M:is_limited() | |
ngx.log(ngx.INFO, "ratelimiter: checking for key=" .. self.key) | |
-- 连接 redis | |
local red, err = redis:new() | |
if red == nil then | |
ngx.log(ngx.ERR, "ratelimiter: redis new error:" .. err) | |
return false | |
end | |
-- 设置连接 redis 的超时时间 | |
red:set_timeout(redis_config.connect_timeout) | |
-- 建立连接 | |
local ok, err = red:connect(redis_config.host, redis_config.port) | |
if not ok then | |
if err ~= nil then | |
ngx.log(ngx.ERR, "ratelimiter: redis connect error:" .. err) | |
end | |
return false | |
end | |
-- 密码认证 | |
if redis_config.password ~= nil then | |
local ok, err = red:auth(redis_config.password) | |
if not ok then | |
if err ~= nil then | |
ngx.log(ngx.ERR, "ratelimiter: redis auth error:" .. err) | |
end | |
return false | |
end | |
end | |
-- 选择 db 索引 | |
red:select(redis_config.db_index) | |
-- 在 redis 中执行 lua 脚本 | |
ngx.log(ngx.INFO, "ratelimiter: redis eval with key:" .. self.key .. ",fill_count:" .. self.fill_count .. | |
",interval_microsecond:" .. self.interval_microsecond .. | |
",bucket_capacity:" .. self.bucket_capacity .. ",expire_second:" .. self.expire_second) | |
local res, err = red:eval(self.script, 1, self.key, self.bucket_capacity, self.fill_count, self.interval_microsecond, self.expire_second) | |
if err ~= nil then | |
ngx.log(ngx.ERR, "ratelimiter: redis eval err:" .. err) | |
return false | |
elseif res == nil then | |
ngx.log(ngx.ERR, "ratelimiter: redis eval return nil res") | |
return false | |
end | |
ngx.log(ngx.DEBUG, "ratelimiter: redis eval return:" .. res ) | |
-- 将 redis 连接放回连接池 | |
local ok, err = red:set_keepalive(redis_config.pool_max_idle_time, redis_config.pool_size) | |
if not ok and err ~= nil then | |
ngx.log(ngx.ERR, "ratelimiter: redis set_keepalive err:" .. err) | |
end | |
-- 处理脚本返回结果 | |
local jsondata = utils.json_decode(res) | |
if jsondata == nil then | |
ngx.log(ngx.ERR, "ratelimiter: redis eval return json decode failed:", res) | |
return false | |
end | |
if jsondata['is_limited'] == true then | |
ngx.log(ngx.ERR, "ratelimiter: hit! key=" .. self.key .. " is limited on threshold=" .. self.bucket_capacity .. " interval_microsecond=", self.interval_microsecond, " res=", res) | |
return true | |
end | |
return false | |
end | |
-- 需要在 redis 中使用 eval 执行的 lua 脚本内容 | |
-- eval 的脚本只能单个值,因此返回 json 字符串. is_limited : false 不限频, true 限频 | |
_M.script = [[ | |
-- 兼容低版本 redis 手动打开允许随机写入 (执行 TIME 指令获取时间) | |
-- 避免报错 Write commands not allowed after non deterministic commands. Call redis.replicate_commands() at the start of your script in order to switch to single commands replication mode. | |
-- Redis 出于数据一致性考虑,要求脚本必须是纯函数的形式,也就是说对于一段 Lua 脚本给定相同的参数,重复执行其结果都是相同的。 | |
-- 这个限制的原因是 Redis 不仅仅是单机版的内存数据库,它还支持主从复制和持久化,执行过的 Lua 脚本会复制给 slave 以及持久化到磁盘,如果重复执行得到结果不同,那么就会出现内存、磁盘、 slave 之间的数据不一致,在 failover 或者重启之后造成数据错乱影响业务。 | |
-- 如果执行过非确定性命令(也就是 TIME ,因为时间是随机的), Redis 就不允许执行写命令,以此来保证数据一致性。 | |
-- 在 Redis 中 time 命令是一个随机命令(时间是变化的),在 Lua 脚本中调用了随机命令之后禁止再调用写命令, Redis 中一共有 10 个随机类命令: | |
-- spop 、 srandmember 、 sscan 、 zscan 、 hscan 、 randomkey 、 scan 、 lastsave 、 pubsub 、 time | |
-- 在执行 redis.replicate_commands() 之后, Redis 就不再是把整个 Lua 脚本同步给 slave 和持久化,而是只把脚本中的写命令使用 multi/exec 包裹后直接去做复制,那么 slave 和持久化只复制了写命名,而写入的也是确定的结果。 | |
redis.replicate_commands() | |
redis.log(redis.LOG_DEBUG, "------------ ratelimiter script begin ------------") | |
-- 获取参数 | |
local p_key = KEYS[1] | |
local p_bucket_capacity = tonumber(ARGV[1]) | |
local p_fill_count = tonumber(ARGV[2]) | |
local p_interval_microsecond = tonumber(ARGV[3]) | |
local p_expire_second = tonumber(ARGV[4]) | |
-- 返回结果 | |
local result = {} | |
result['p_key'] = p_key | |
result['p_fill_count'] = p_fill_count | |
result['p_bucket_capacity'] = p_bucket_capacity | |
result['p_interval_microsecond'] = p_interval_microsecond | |
result['p_expire_second'] = p_expire_second | |
-- 每次填充 token 数为 0 或 令牌桶容量为 0 则表示限制该请求 直接返回 无需操作 redis | |
if p_fill_count <= 0 or p_bucket_capacity <= 0 then | |
result['msg'] = "be limited by p_fill_count or p_bucket_capacity" | |
result['is_limited'] = true | |
return cjson.encode(result) | |
end | |
-- 判断桶是否存在 | |
local exists = redis.call("EXISTS", p_key) | |
redis.log(redis.LOG_DEBUG, "ratelimiter: key:" .. p_key .. ", exists:" .. exists) | |
-- 桶不存在则在 redis 中创建桶 并消耗当前 token | |
if exists == 0 then | |
-- 本次填充时间戳 | |
local now_timestamp_array = redis.call("TIME") | |
-- 微秒级时间戳 | |
local last_consume_timestamp = tonumber(now_timestamp_array[1]) * 1000000 + tonumber(now_timestamp_array[2]) | |
redis.log(redis.LOG_DEBUG, "ratelimiter: last_consume_timestamp:" .. last_consume_timestamp .. ", remain_token_count:" .. p_bucket_capacity) | |
-- 首次请求 默认为满桶 消耗一个 token | |
local remain_token_count = p_bucket_capacity - 1 | |
-- 将当前秒级时间戳和剩余 token 数保存到 redis | |
redis.call("HMSET", p_key, "last_consume_timestamp", last_consume_timestamp, "remain_token_count", remain_token_count) | |
-- 设置 redis 的过期时间 | |
redis.call("EXPIRE", p_key, p_expire_second) | |
redis.log(redis.LOG_DEBUG, "ratelimiter: call HMSET for creating bucket") | |
redis.log(redis.LOG_DEBUG, "------------ ratelimiter script end ------------") | |
-- 保存 result 信息 | |
result['msg'] = "key not exists in redis" | |
-- string format 避免科学计数法 | |
result['last_consume_timestamp'] = string.format("%18.0f", last_consume_timestamp) | |
result['remain_token_count'] = remain_token_count | |
result['is_limited'] = false | |
return cjson.encode(result) | |
end | |
-- 桶存在时,重新计算填充 token | |
-- 获取 redis 中保存的上次填充时间和剩余 token 数 | |
local array = redis.call("HMGET", p_key, "last_consume_timestamp", "remain_token_count") | |
if array == nil then | |
redis.log(redis.LOG_WARNING, "ratelimiter: HMGET return nil for key:" .. p_key) | |
redis.log(redis.LOG_DEBUG, "------------ ratelimiter script end ------------") | |
-- 保存 result 信息 | |
result['msg'] = "err:HMGET data return nil" | |
result['is_limited'] = false | |
return cjson.encode(result) | |
end | |
local last_consume_timestamp, remain_token_count = tonumber(array[1]), tonumber(array[2]) | |
redis.log(redis.LOG_DEBUG, "ratelimiter: last_consume_timestamp:" .. last_consume_timestamp .. ", remain_token_count:" .. remain_token_count) | |
-- 计算当前时间距离上次填充 token 过了多少微秒 | |
local now_timestamp_array = redis.call("TIME") | |
local now_timestamp = tonumber(now_timestamp_array[1]) * 1000000 + tonumber(now_timestamp_array[2]) | |
local duration_microsecond = math.max(now_timestamp - last_consume_timestamp, 0) | |
-- 根据配置计算 token 的填充速率: x token/μs | |
local fill_rate = p_fill_count / p_interval_microsecond | |
redis.log(redis.LOG_DEBUG, "ratelimiter: now_timestamp:" .. now_timestamp .. ", duration_microsecond:" .. duration_microsecond .. ", fill_rate:" .. fill_rate) | |
-- 计算在这段时间内产生了多少 token , 浮点数向下取整 | |
local fill_token_count = math.floor(fill_rate * duration_microsecond) | |
-- 计算桶内当前时间应有的 token 总数,总数不超过桶的容量 | |
local now_token_count = math.min(remain_token_count + fill_token_count, p_bucket_capacity) | |
redis.log(redis.LOG_DEBUG, "ratelimiter: fill_token_count:" .. fill_token_count .. ", now_token_count:" .. now_token_count) | |
-- 保存 debug 信息 | |
result['last_consume_timestamp'] = string.format("%18.0f", last_consume_timestamp) | |
result['remain_token_count'] = remain_token_count | |
result['now_timestamp'] = string.format("%18.0f", now_timestamp) | |
result['duration_microsecond'] = string.format("%18.0f", duration_microsecond) | |
result['fill_rate'] = string.format("%18.9f", fill_rate) | |
result['fill_token_count'] = fill_token_count | |
result['now_token_count'] = now_token_count | |
-- 无可用 token | |
if now_token_count <= 0 then | |
-- 更新 redis 中的数据,被限流不消耗 now_token_count | |
redis.call("HMSET", p_key, "last_consume_timestamp", last_consume_timestamp, "remain_token_count", now_token_count) | |
-- 设置 redis 的过期时间 | |
redis.call("EXPIRE", p_key, p_expire_second) | |
redis.log(redis.LOG_DEBUG, "ratelimiter: call HMSET for updating bucket") | |
redis.log(redis.LOG_DEBUG, "------------ ratelimiter script end ------------") | |
result['msg'] = "limit" | |
result['is_limited'] = true | |
return cjson.encode(result) | |
end | |
-- 更新 redis 中的数据, 消耗一个 token | |
redis.call("HMSET", p_key, "last_consume_timestamp", now_timestamp, "remain_token_count", now_token_count - 1) | |
-- 设置 redis 的过期时间 | |
redis.call("EXPIRE", p_key, p_expire_second) | |
redis.log(redis.LOG_DEBUG, "ratelimiter: call HMSET for updating bucket") | |
redis.log(redis.LOG_DEBUG, "------------ ratelimiter script end ------------") | |
result['msg'] = "pass" | |
result['is_limited'] = false | |
return cjson.encode(result) | |
]] | |
return _M |